NBER Working Paper No. 22501
Issued in August 2016
NBER Program(s): ED LS
We develop a new dataset using UNESCO source materials on the location of nearly 15,000 universities in about 1,500 regions across 78 countries, some dating back to the 11th Century. We estimate fixed effects models at the sub-national level between 1950 and 2010 and find that increases in the number of universities are positively associated with future growth of GDP per capita (and this relationship is robust to controlling for a host of observables, as well as unobserved regional trends). Our estimates imply that doubling the number of universities per capita is associated with 4% higher future GDP per capita. Furthermore, there appear to be positive spillover effects from universities to geographically close neighboring regions. We show that the relationship between growth and universities is not simply driven by the direct expenditures of the university, its staff and students. Part of the effect of universities on growth is mediated through an increased supply of human capital and greater innovation (although the magnitudes are not large). We find that within countries, higher historical university presence is associated with stronger pro-democratic attitudes.
Nem található esemény a közeljövőben.
A KRTK Közgazdaság-tudományi Intézet teljesítményéről A KRTK KTI a RePEc/IDEAS rangsorában, amely a világ közgazdaság-tudományi tanszékeit és intézeteit rangsorolja publikációs teljesítményük alapján, a legjobb ... Read More »

Tisztelt Kollégák! Tudományos kutatóként, intézeti vezetőként egész életünkben a kutatói szabadság és felelősség elve vezetett bennünket. Meggyőződésünk, hogy a tudomány csak akkor érhet el ... Read More »

Srí Lanka: a 2022-es gazdasági válság leckéje – A. Krueger Lessons from Sri Lanka Anne O. Krueger Jul 25, 2022 – Project Syndicate ... Read More »

A permanens válság korában élünk – J. Meadway We’re living in an age of permanent crisis – let’s stop planning for a ‘return ... Read More »
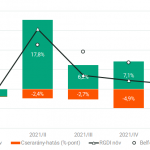
A 2021 végén, illetve 2022 elején tapaszalt 6, illetve 7%-os cserearányromlás brutális reáljövedelem-kivonást jelentett a magyar gazdaságból. A külső egyensúly alakulásával foglalkozó elemzések többnyire ... Read More »
