
Vonnák Dzsamila Why do firms default on their foreign currency loans? The case of Hungary című cikke Journal of International Money and Finance szeptemberi számában:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0261560618302766?via%3Dihub
I isolate the effect of the choice of foreign currency on the loan performance of firms borrowing in different currencies in crisis times. I use a novel micro-level dataset from Hungary to decompose the factors contributing to the worse loan performance of foreign currency borrowers compared to local currency debtors. I find that foreign currency denomination can worsen loan performance considerably, while selection also contributes significantly to the default differences. On the one hand, per se less creditworthy firms borrowed in foreign currency and during the crisis the foreign currency shocks further weakened their loan performances. On the other hand, more creditworthy firms that were also well-prepared for the currency risks also borrowed in foreign currency. My results suggest that not the institution of foreign currency lending per se that should be blamed for the bad loan performance of foreign currency borrowers, instead one should consider the characteristics of the borrowers.
Nem található esemény a közeljövőben.
A KRTK Közgazdaság-tudományi Intézet teljesítményéről A KRTK KTI a RePEc/IDEAS rangsorában, amely a világ közgazdaság-tudományi tanszékeit és intézeteit rangsorolja publikációs teljesítményük alapján, a legjobb ... Read More »

Tisztelt Kollégák! Tudományos kutatóként, intézeti vezetőként egész életünkben a kutatói szabadság és felelősség elve vezetett bennünket. Meggyőződésünk, hogy a tudomány csak akkor érhet el ... Read More »

Srí Lanka: a 2022-es gazdasági válság leckéje – A. Krueger Lessons from Sri Lanka Anne O. Krueger Jul 25, 2022 – Project Syndicate ... Read More »

A permanens válság korában élünk – J. Meadway We’re living in an age of permanent crisis – let’s stop planning for a ‘return ... Read More »
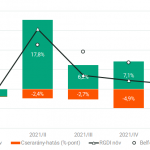
A 2021 végén, illetve 2022 elején tapaszalt 6, illetve 7%-os cserearányromlás brutális reáljövedelem-kivonást jelentett a magyar gazdaságból. A külső egyensúly alakulásával foglalkozó elemzések többnyire ... Read More »
