Abstract:
Since trust correlates with economic development and in turn economic development associates with political regime, we conjecture that there may be a relationship between trust and political regime. Without looking for any casual inference, we investigate if trust aggregated on the country level correlates with the country’s political regime. Specifically, we are interested whether trust correlates positively with the level of democracy in cross-sectional observations. We analyse data on trust from 76 countries using the Global Preference Survey and investigate the correlations with five separate democracy indices (Polity2, Economist Intelligence Unit’s Index of Democracy, Freedom House, MaxRange and Unified Democracy Score). We do not find any significant association, with or without taking into account other factors (e.g., regional location, economic development, geographic conditions, culture) as well. Trust does not correlate with cornerstones of democracy either, measured by five components of the EIU index. A robustness check using an alternative measure of trust from the World Values Survey reaches the same results. The present study supersedes the working paper version (Khayouti et al., 2020).
Nem található esemény a közeljövőben.
A KRTK Közgazdaság-tudományi Intézet teljesítményéről A KRTK KTI a RePEc/IDEAS rangsorában, amely a világ közgazdaság-tudományi tanszékeit és intézeteit rangsorolja publikációs teljesítményük alapján, a legjobb ... Read More »

Tisztelt Kollégák! Tudományos kutatóként, intézeti vezetőként egész életünkben a kutatói szabadság és felelősség elve vezetett bennünket. Meggyőződésünk, hogy a tudomány csak akkor érhet el ... Read More »

Srí Lanka: a 2022-es gazdasági válság leckéje – A. Krueger Lessons from Sri Lanka Anne O. Krueger Jul 25, 2022 – Project Syndicate ... Read More »

A permanens válság korában élünk – J. Meadway We’re living in an age of permanent crisis – let’s stop planning for a ‘return ... Read More »
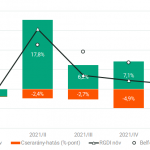
A 2021 végén, illetve 2022 elején tapaszalt 6, illetve 7%-os cserearányromlás brutális reáljövedelem-kivonást jelentett a magyar gazdaságból. A külső egyensúly alakulásával foglalkozó elemzések többnyire ... Read More »
