NBER Working Paper No. 21777
Issued in December 2015
NBER Program(s): DAE
A large literature has documented an association between economic growth and export diversification. We study this question in France between 1836 and 1938. The period witnessed the onset of modern economic growth and sharp changes in the level of international competition. We use a new long term database on French foreign trade at a high level of disaggregation. At the dawn of the first Globalization, France appears to have specialized along Ricardian lines, exporting a handful of textile products in large quantities. There is a decrease in specialization from 1860 to World War I along the lines of modern studies. Changes in trade costs along with economic growth help explain the evolution of France’s comparative advantage. The decline of export concentration is associated with a chronic deficit in the balance of trade during the Belle Époque and the major part of the interwar period particularly after 1927. This paper is available as PDF (301 K) .
Nem található esemény a közeljövőben.
A KRTK Közgazdaság-tudományi Intézet teljesítményéről A KRTK KTI a RePEc/IDEAS rangsorában, amely a világ közgazdaság-tudományi tanszékeit és intézeteit rangsorolja publikációs teljesítményük alapján, a legjobb ... Read More »

Tisztelt Kollégák! Tudományos kutatóként, intézeti vezetőként egész életünkben a kutatói szabadság és felelősség elve vezetett bennünket. Meggyőződésünk, hogy a tudomány csak akkor érhet el ... Read More »

Srí Lanka: a 2022-es gazdasági válság leckéje – A. Krueger Lessons from Sri Lanka Anne O. Krueger Jul 25, 2022 – Project Syndicate ... Read More »

A permanens válság korában élünk – J. Meadway We’re living in an age of permanent crisis – let’s stop planning for a ‘return ... Read More »
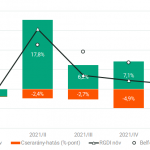
A 2021 végén, illetve 2022 elején tapaszalt 6, illetve 7%-os cserearányromlás brutális reáljövedelem-kivonást jelentett a magyar gazdaságból. A külső egyensúly alakulásával foglalkozó elemzések többnyire ... Read More »
