NBER Working Paper No. 21672
Issued in October 2015
NBER Program(s): EFG
We discuss business cycles in ancient China. Data on Ancient China business cycles are sparse and incomplete and so our discussion is qualitative rather than quantitative. Essentially, ancient debates focused on two types of cycles: long run political or dynastic cycles of many decades, and short run nature induced cycles. Discussion of the latter show strong parallels to Jevons’ conception of sun spot cycles. The former has no clear contemporary analogue, were often deep in impact and of long duration. The discussion of both focused on agricultural economies. Ancient discussion on intervention focused on counter cyclical measures, including stockpiling, and predated Keynes and the discussion in the 1930s by centuries. Also, a strongly held belief emerged that cycles create their own cycles to follow, and that cycles are part of the inevitable economic order, a view consistent with Mitchell’s view of the business cycle in the 1940s. Current debates on how best to respond to the ongoing global financial crisis draw in part on historical precedents, but these are largely limited to the last 150 years for OECD countries and with major focus on the 1990’s. Here we also probe material on Ancient China to see what is relevant. This paper is available as PDF (739 K).
Nem található esemény a közeljövőben.
A KRTK Közgazdaság-tudományi Intézet teljesítményéről A KRTK KTI a RePEc/IDEAS rangsorában, amely a világ közgazdaság-tudományi tanszékeit és intézeteit rangsorolja publikációs teljesítményük alapján, a legjobb ... Read More »

Tisztelt Kollégák! Tudományos kutatóként, intézeti vezetőként egész életünkben a kutatói szabadság és felelősség elve vezetett bennünket. Meggyőződésünk, hogy a tudomány csak akkor érhet el ... Read More »

Srí Lanka: a 2022-es gazdasági válság leckéje – A. Krueger Lessons from Sri Lanka Anne O. Krueger Jul 25, 2022 – Project Syndicate ... Read More »

A permanens válság korában élünk – J. Meadway We’re living in an age of permanent crisis – let’s stop planning for a ‘return ... Read More »
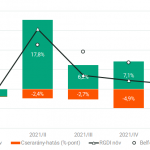
A 2021 végén, illetve 2022 elején tapaszalt 6, illetve 7%-os cserearányromlás brutális reáljövedelem-kivonást jelentett a magyar gazdaságból. A külső egyensúly alakulásával foglalkozó elemzések többnyire ... Read More »
